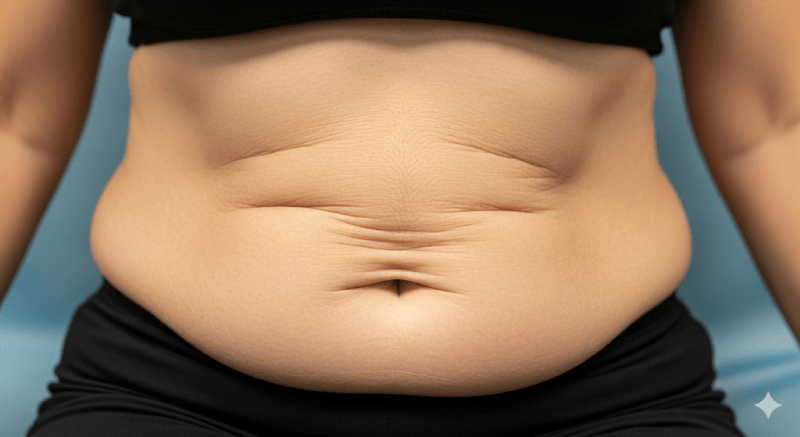
Sleeve gastrectomy (gastric sleeve) surgery is an effective method for treating obesity as it provides significant and rapid weight loss. However, it is not always easy for the body to adapt to this rapid change, and one of the most common side effects is skin sagging.
Causes and Process of Skin Sagging
Skin sagging after sleeve gastrectomy is a physiological condition that arises depending on the amount and speed of weight lost. The main reason is the loss of skin elasticity. The skin is an organ with the ability to stretch and contract. When a person is overweight for a long time, the underlying fat tissue stretches the skin, and the structure of collagen and elastin fibers weakens. When rapid weight loss occurs, these tissues shrink, but the skin cannot contract at the same speed, and as a result, sagging occurs in areas that have lost their elasticity.
Common Areas of Skin Sagging and Risk Factors
Skin sagging is more pronounced in areas of the body that store more fat and where the skin is stretched more. These areas typically include:
- Abdomen: This is the most common area.
- Breasts
- Arms (bat wings)
- Thighs (inner legs)
- Face and neck
Factors that increase the risk of skin sagging are:
- Amount of weight lost: The more weight lost, the higher the risk of sagging.
- Age: As age progresses, the production of collagen and elastin in the skin decreases, leading to a loss of elasticity.
- Genetic predisposition: An individual’s genetic makeup directly affects the degree of skin elasticity.
- Rapid weight loss: Rapid weight loss does not give the skin a chance to regenerate.
- Smoking: Smoking damages collagen production by impairing blood flow.
- Sun exposure: Excessive sun exposure accelerates skin aging and the loss of elasticity.
Rate of Weight Loss and Pre-surgery Skin Elasticity
There is a significant difference in sagging between rapid weight loss and slow weight loss. With rapid weight loss, the skin struggles to keep up with the shrinking body, and sagging becomes more common and severe. With slow weight loss, the skin has a better chance to recover.
Pre-surgery skin elasticity also directly affects post-surgery sagging. Sagging may be less in individuals with younger, more elastic skin, while it may be more pronounced in older people or those who have repeatedly gained and lost weight.
Preventive Measures and Nutrition
Some steps taken before or after surgery can help reduce the risk of sagging:
- Proper Nutrition: It is important to prioritize foods that support skin health. Protein, in particular, is the main building block for collagen production. Protein intake should be increased with foods such as fish, chicken, eggs, dairy products, and legumes. Additionally, antioxidants like Vitamin C (citrus fruits, red peppers, broccoli), Vitamin E (nuts, avocado), and zinc (pumpkin seeds, red meat) are critical for skin health.
- Exercise: After surgery, with your doctor’s approval, you can start with light exercises such as walking, and later move on to weight training and resistance exercises. These exercises help to increase muscle mass, filling the space under the skin and providing a firmer appearance.
- Collagen Supplements: There is no direct proven benefit of collagen supplements in preventing skin sagging. However, they can be used to supplement the nutrition program. It is essential to consult with a specialist before using such supplements.
Treatment Methods and Surgeries
Sagging skin is not only an aesthetic problem but can also lead to irritation, infections, and hygiene issues. The accumulation of sweat under sagging skin creates a suitable environment for the growth of fungi and bacteria.
Non-surgical treatment methods (such as laser, radiofrequency, and ultrasound) can be effective for mild sagging but may be insufficient to address the severe sagging that occurs after rapid and significant weight loss.
The most effective method for permanent removal of sagging skin is aesthetic surgery. The main surgical methods applied are:
- Body Lift Surgery: This surgery is designed to remove excess skin and fat from multiple areas such as the abdomen, buttocks, thighs, and back. The ideal timing for this surgery is when weight loss has stopped and body weight has remained stable for at least 6-12 months. This ensures the body is fully ready for the surgery and reduces the risk of recurrent sagging.
- Arm Lift (Brachioplasty)
- Thigh Lift (Thigh Lift)
- Breast Lift (Mastopexy)
These surgical interventions are generally planned in stages depending on the patient’s condition and needs. Operations involving multiple areas can be performed at different times, considering the patient’s health and recovery process. The risks of body lift surgeries include infection, bleeding, and wound healing problems. The recovery period varies depending on the size of the operation.
Psychological Impact and Expert Consultation
Sagging skin can lower patients’ self-esteem and have a negative psychological impact. Issues such as body image problems, social withdrawal, and depression can be seen. Therefore, in addition to physical health, psychological support is also important.
Smoking and alcohol use are extremely harmful to skin health after sleeve gastrectomy. Smoking impairs blood flow, slowing down wound healing and inhibiting collagen production.
For skin sagging after sleeve gastrectomy, a plastic, reconstructive, and aesthetic surgery specialist should be consulted. These specialists will evaluate the patient’s general health, weight loss, and skin structure to determine the most suitable treatment plan.