What Is Gastric Balloon Treatment?
Gastric balloon treatment is a non-surgical, minimally invasive method used in the treatment of obesity. In this procedure, an inflatable balloon made of materials like silicone or polyurethane is placed inside the stomach. The balloon aims to increase the feeling of fullness by occupying a certain amount of space in the stomach, thus helping the person eat less. This method can be an effective alternative for individuals who are hesitant about surgical operations or are not suitable for surgery. It typically remains in the stomach for six months to a year, during which it helps the patient lose weight.
How Does the Gastric Balloon Work?
The balloon placed in the stomach works by physically reducing the stomach’s volume. By occupying approximately one-third of the stomach cavity, the balloon helps the digestive system send a quicker signal of satiety. This enables the person to reduce their food portions and decreases the urge to snack between meals. Furthermore, the presence of the balloon slows down the rate of digestion, which makes the feeling of fullness last longer. The mechanical effect of the balloon not only helps control the amount of food consumed but also creates a “practice ground” for the patient to adopt healthy eating habits.
Who Is a Suitable Candidate for Gastric Balloon?
Gastric balloon treatment is generally considered a suitable option for individuals with a body mass index (BMI) between 27 and 40 who have not been able to achieve sufficient weight loss through diet and exercise programs. This procedure is ideal for patients who have a high risk for surgical operations or do not want surgical intervention. However, it may not be suitable for those who have previously had stomach or esophageal surgery, stomach ulcers, or severe reflux disease. Candidacy must always be evaluated by a team of specialists, including a gastroenterologist, a dietitian, and a psychologist.
What Are the Types of Gastric Balloons? (Endoscopic Balloons)
Gastric balloons are divided into two main categories based on their application methods. Endoscopic balloons are placed into the stomach using an endoscope under sedation (a light state of sleep). During this procedure, the folded balloon is guided into the stomach and then inflated with saline (salt water) or air. The biggest advantage of these types of balloons is that the placement and removal procedures are performed under the controlled supervision of a physician. They can be designed to stay in the stomach for an average of 6 or 12 months and are typically removed with an endoscope at the end of this period.
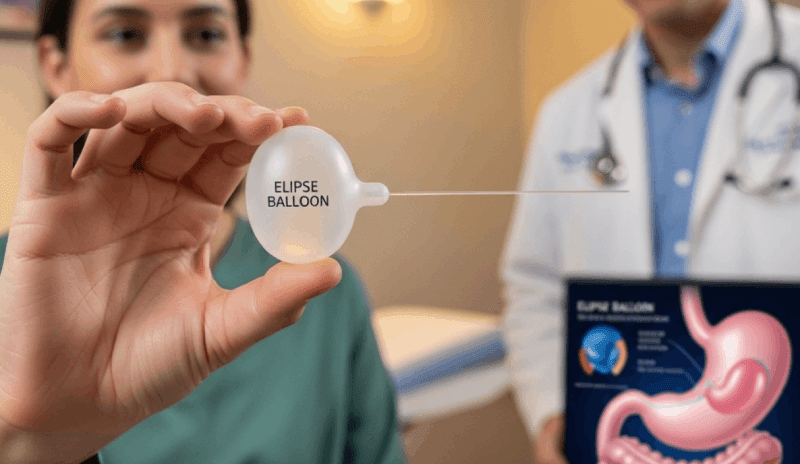
Swallowable Gastric Balloon (Elipse Balloon)
The swallowable gastric balloon is an innovative treatment method that does not require endoscopy or anesthesia. The patient swallows the balloon, which is enclosed in a capsule the size of a pill, with water. Once the capsule reaches the stomach, it is inflated with a liquid controlled by the doctor via a thin catheter. This procedure usually takes about 20 minutes. After four months, the balloon has a self-sealing release valve that allows it to deflate on its own. The deflated balloon is then passed naturally out of the body. This makes it an attractive option for patients who wish to avoid endoscopy or surgical operations.
Preparation Process and Initial Assessment
Before starting gastric balloon treatment, the patient’s overall health status is comprehensively assessed. This process is critical for the success and safety of the treatment. The initial assessment includes a detailed examination of the patient’s eating habits, psychological state, medical history, and weight history. It is determined whether the candidate’s expectations from the treatment are realistic and how motivated they are to make lifestyle changes. This stage is important to understand if the patient can adhere to the treatment plan.
Consultation with a Dietitian and Nutritionist
The success of gastric balloon treatment does not solely depend on the presence of the balloon. The patient must fundamentally change their eating habits. Therefore, working with a dietitian before and after the treatment is mandatory. The dietitian teaches the patient the necessary nutrition plan to follow with the balloon, which foods to consume and which to avoid, and how to practice portion control. Regular follow-ups during the treatment period ensure that healthy eating habits become permanent.
Psychological Evaluation and Counseling
Obesity is often associated with psychological factors. Conditions such as emotional eating, coping mechanisms for stress, or eating disorders can negatively affect the weight loss process. For this reason, it is recommended to have an evaluation by a psychologist or psychiatrist before gastric balloon treatment. Psychological support helps the patient maintain high motivation, cope with difficulties, and achieve their weight loss goals.
Necessary Medical Tests and Check-ups
To ensure the safe application of the treatment, some basic medical tests are performed on the patient. These tests typically include a complete blood count, kidney and liver function tests, thyroid hormones, and blood sugar levels. In some cases, additional tests such as an endoscopy may be requested to check the condition of the stomach and esophagus. These check-ups are done to identify any hidden health problems in the patient and minimize the risks of the procedure.

Preparation for the Procedure Day
On the day of the procedure, it is important for patients to arrive with a calm mind. According to the doctor’s instructions, it is necessary to abstain from eating and drinking fluids for a certain period before the procedure. This period is usually around 6-12 hours. It is recommended that the patient wear comfortable clothes and bring a companion. Final checks are performed before the procedure, and the patient is informed about how the procedure will proceed.
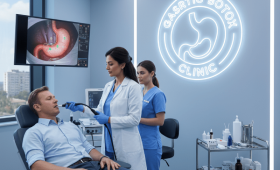
Endoscopic Placement of the Balloon
The endoscopic gastric balloon placement procedure is usually performed in a hospital or clinic setting. Before the procedure, the patient is given light sedation to ensure they are relaxed and do not feel any pain. The doctor advances a thin, flexible tube called an endoscope through the mouth into the stomach. Once it reaches an appropriate position in the stomach, the folded balloon is released through the endoscope and inflated to the desired size with a liquid or air. The procedure takes a total of about 20-30 minutes.
Application of the Swallowable Balloon
The application of the swallowable balloon is quite simple and does not require an endoscopy. The patient swallows the pill-sized balloon with a glass of water. The capsule is connected to a thin catheter. Once the capsule reaches the stomach, its correct position is confirmed with an X-ray or ultrasound imaging. Then, liquid is filled into the balloon through the catheter. When the procedure is complete, the catheter is gently withdrawn. This method is a comfortable and fast alternative for the patient.
What Is Felt During the Procedure?
During endoscopic balloon placement, patients typically do not feel anything because they are under sedation. After the procedure, they may feel a slight grogginess and a mild discomfort in the throat. In the case of the swallowable balloon application, the patient is fully awake. They may feel a slight discomfort while swallowing the balloon, but the procedure is generally painless. When the balloon is inflated, there may be a mild feeling of fullness in the stomach, which is an indication of the balloon’s function.
First Hours and Observation After the Procedure
After the gastric balloon is placed, patients are usually kept under observation for a few hours. During this period, early side effects such as nausea, vomiting, or abdominal cramps are monitored. These symptoms are normal and usually pass in a short time. The nurse or doctor provides the patient with the necessary medications and instructions to manage the side effects. The patient remains at the clinic until they feel well enough to return home.
First 24-48 Hour Period: Side Effects and Management
The first 1-2 days after the procedure can be the most challenging period. The body tries to adapt to the balloon inside the stomach. During this process, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and pain are common. Anti-nausea and pain-relief medications prescribed by the doctor help alleviate these symptoms. Food and fluid intake are very limited during this period, and the patient is advised to rest as much as possible.
Liquid Diet Period: The First Week
The first week after gastric balloon treatment is a period of consuming only liquid foods. This allows the stomach time to adapt. It starts with clear liquids (water, unsweetened tea, compote juice) and then moves on to thicker liquids like milk, buttermilk, and soups without solids. It is very important to drink slowly and in small sips during this period. Care should be taken to ensure adequate fluid intake to prevent dehydration.
Puréed Diet Period: Second and Third Week
After a week of a liquid diet, the patient transitions to puréed foods. At this stage, items like yogurt, vegetable purée, puréed fruits, and well-cooked, puréed proteins (chicken, fish) are included in the menu. Portions should still be very small. It is important to avoid spicy, greasy, and high-fiber foods to prevent them from being heavy on the stomach.
Transition to Normal Eating: Fourth Week and Beyond
From the fourth week of treatment, a gradual transition to solid foods is made under the supervision of a dietitian. At this stage, small portions of well-chewed and slowly consumed foods should be preferred. Patients are encouraged to adopt a healthy and balanced diet. This is one of the most important factors determining the long-term success of the treatment.
Duration of the Gastric Balloon in the Body
Gastric balloon types can remain in the stomach for different durations, depending on their design. Balloons are typically designed to stay for 6 or 12 months. Swallowable balloons, on the other hand, have the feature to deflate on their own after 4 months. At the end of the specified period, the balloon is removed via endoscopy. This duration provides enough time for you to achieve your weight loss goals with gastric balloon treatment.
Balloon Removal: Procedure and Process
The gastric balloon removal procedure, like its placement, is performed with an endoscope. The procedure is generally done under sedation. The doctor uses the endoscope to reach the stomach and empties the liquid inside the balloon with the help of a catheter. The deflated balloon is then taken out through the mouth with the help of the endoscope. This procedure also takes about 20-30 minutes and is generally painless.
Expected Weight Loss Rates
The expected weight loss in gastric balloon treatment varies depending on the patient’s initial weight and their adherence to diet and exercise habits. Generally, patients can experience a weight loss of between 10% and 25% of their total body weight. The weight loss occurs most rapidly during the period the balloon remains in the stomach. If a healthy lifestyle is maintained after the balloon is removed, weight maintenance is possible.
The Key to Long-Term Success: Lifestyle Changes
The gastric balloon is only a tool; the real success depends on the patient making permanent lifestyle changes. These changes include regular exercise, a balanced diet, portion control, and healthy eating habits. Returning to old eating habits after the balloon is removed can cause the lost weight to be regained. Therefore, maintaining the habits acquired during the treatment is of critical importance.
Possible Risks, Complications, and Side Effects
As with any medical procedure, gastric balloon treatment has some risks. The most common side effects are nausea, vomiting, and abdominal cramps, which usually pass within the first few days. More rare but serious complications can include balloon rupture, gastric obstruction, or ulcer formation. These risks can be minimized by the experience of the physician performing the treatment and the patient’s adherence to instructions.
Gastric Balloon and Exercise: The Importance of Physical Activity
Gastric balloon treatment is more effective when supported by physical activity. Regular exercise speeds up metabolism, preserves muscle mass, and helps with weight loss. In the first days of treatment, light walks are recommended, while the intensity of exercise can be gradually increased in the following weeks. Activities such as going to the gym, swimming, cycling, or walking should be an integral part of the treatment process.
Life After Gastric Balloon: Support and Follow-up
Patient follow-up should continue even after the balloon is removed. The support of a dietitian, psychologist, and doctor plays a major role in helping the patient achieve their weight maintenance goals. Support groups or individual counseling sessions are beneficial for coping with difficulties and maintaining high motivation. Gastric balloon treatment is a starting point for a transition to a new and healthier life.