Gum Bleeding: Causes and Treatment Methods
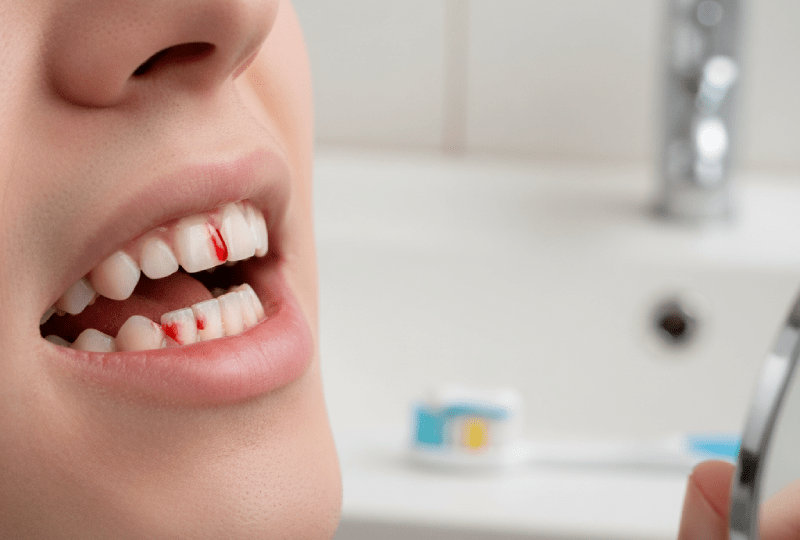
Gum bleeding is one of the most common signs of oral health problems and is often an indicator of gingivitis (gum inflammation). It can occur even during light brushing or flossing. The main cause of gum bleeding is a sticky layer called plaque which consists of bacteria and food debris that accumulates between the teeth and gums. When plaque is not cleaned, it hardens into tartar or dental calculus and causes further irritation to the gums.
Understanding the underlying causes of gum bleeding is vital to determine the correct treatment method. This article provides a comprehensive look at the causes, effective treatment methods, and prevention of gum bleeding.
Main Causes of Gum Bleeding
Although the most common cause of gum bleeding is plaque buildup, other factors can also lead to this condition:
- Incorrect Brushing Technique: Brushing too hard or at the wrong angle can damage the gums.
- Incorrect Flossing Technique: Applying too much pressure with floss on the gums can cause bleeding.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations such as during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can make the gums more sensitive.
- Vitamin Deficiency: Vitamin C and K deficiency can negatively affect gum health.
- Certain Medications: Blood thinners or some blood pressure medications can increase gum bleeding.
- Systemic Diseases: Certain diseases like diabetes and leukemia can trigger gum bleeding.
- Smoking: Smoking reduces blood flow to the gums, increasing the risk of infection.
Home Treatment Methods
Gum bleeding can often be controlled with simple home care methods. These methods help to reduce gum inflammation and stop the bleeding:
- Proper Brushing and Flossing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and proper brushing technique. Gently use dental floss to clean between your teeth.
- Salt Water Rinse: Rinsing with warm salt water helps to reduce inflammation and bacteria in the mouth. Add half a teaspoon of salt to a glass of warm water and rinse several times a day.
- Antiseptic Mouthwash: Using an alcohol-free, antiseptic mouthwash can be beneficial in reducing plaque formation.
- Natural Oils: Some natural oils (for example, tea tree oil) have anti-inflammatory properties. You can add these oils, diluted, to your gargle water.
- Healthy Diet: Eating foods rich in vitamins C and K supports gum health.
Professional Treatment Methods
When home methods are not sufficient or if bleeding is severe, it is mandatory to consult a dentist. The dentist will determine the underlying cause of the bleeding and apply the appropriate professional treatment:
- Dental Scaling (Detartrage): This is the most common treatment for gum bleeding. The dentist uses special tools to clean the plaque and tartar between the teeth and gums.
- Root Planing (Curettage): If gingivitis has advanced, the dentist cleans and smooths the surfaces of the tooth roots to prevent bacterial buildup.
- Antibiotic Treatment: In cases of severe infection, the dentist may recommend oral antibiotics or antibacterial gels.
- Gum Surgery: In cases of advanced gum disease (periodontitis), surgical intervention may be required to shrink gum pockets and stop bone loss.
Preventing Gum Bleeding
Preventing gum bleeding is just as important as treating it. Here are steps you can take to keep your gums healthy:
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Visit your dentist at least twice a year for professional cleaning and early detection of potential problems.
- Proper Oral Hygiene: Develop the habit of brushing twice a day and flossing every day.
- Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet and avoiding smoking are important for your overall health as well as your gum health.
- Change Your Toothbrush: Change your toothbrush every three months.
- Dentist’s Recommendation: Consult your dentist about the most suitable toothpaste and oral care products for your gums.