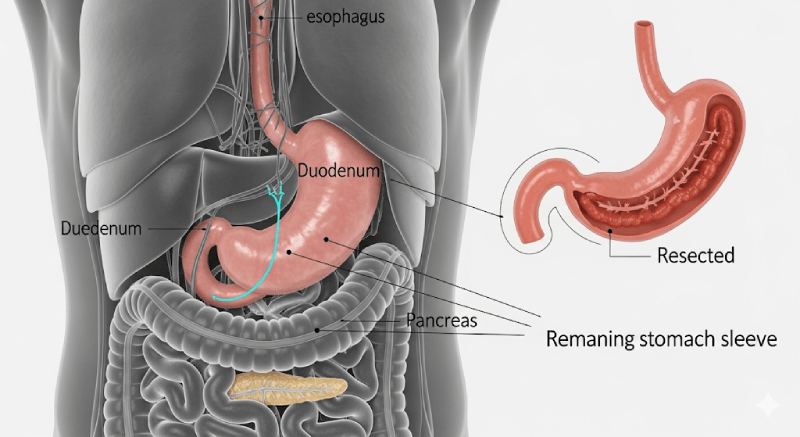
Gastric sleeve surgery is one of the most common and effective surgical methods for treating obesity. This operation, which involves removing approximately 80% of the stomach, helps patients feel full with less food and accelerates the weight loss process. However, as with any surgical procedure, gastric sleeve surgery may not always yield the expected results. So, what happens if gastric sleeve surgery doesn’t work? What are the reasons for this, how are the symptoms recognized, and what solutions can be pursued if this situation is encountered?
What is Gastric Sleeve Surgery Failure?
Several criteria exist for a gastric sleeve surgery to be considered a failure. The most widely accepted criterion is the failure to achieve the expected weight loss after the surgery or the regain of lost weight. Generally, for a gastric sleeve surgery to be considered successful, the patient is expected to lose at least 50% of their excess weight. Failure to meet this goal or regaining some or all of the lost weight within the first 1-2 years after the surgery can mean the operation was unsuccessful. Many factors can underlie this situation, and understanding these factors is crucial for determining the appropriate solutions.
Symptoms of Gastric Sleeve Surgery Failure
Failure after gastric sleeve surgery usually manifests with a series of physical and psychological symptoms. The most prominent of these symptoms are a stall in weight loss (plateau phase) or weight regain. While rapid weight loss is normal in the first few weeks after surgery, an unexpected early halt in this process or, conversely, the beginning of weight regain months or years after the surgery can be alarming.
Other physical symptoms that may accompany this situation include:
- Being able to consume foods that previously caused discomfort more easily.
- The feeling of fullness not being the same as before, and an increased desire to eat.
- Unconsciously increasing portion sizes.
- A frequent need to snack, especially on high-calorie and liquid foods.
Psychologically, patients may experience feelings of failure, disappointment, and hopelessness. Failure to reach the weight loss goal can lead to a loss of motivation and the re-emergence of pre-existing eating disorders or psychological problems. To prevent this, it is essential to closely monitor both physical and psychological symptoms and seek expert support.
Possible Causes of Gastric Sleeve Surgery Failure
The failure of a gastric sleeve surgery cannot be attributed to a single cause; this situation usually results from a combination of multiple factors. The causes can be examined under three main headings: lifestyle, physiological, and technical factors.
Lifestyle and Behavioral Causes
These factors are the most common reasons for failure and are usually due to the patient’s inability to adapt to the new post-surgery lifestyle.
- Poor Eating Habits: Although portion sizes shrink due to the surgery, excessive consumption of high-calorie, sugary, and fatty foods or liquid beverages can lead to weight gain. “Liquid calories” like ice cream, milkshakes, sweet drinks, and chocolate are among the biggest dangers as they can easily fit into the smaller stomach.
- Lack of Sufficient Exercise: Surgery is not a standalone solution. Regular physical activity combined with a healthy diet is vital for both boosting metabolism and preserving muscle mass. A sedentary lifestyle can stall weight loss and set the stage for regaining lost weight.
- Emotional Eating and Psychological Issues: Surgery does not eliminate the psychological reasons behind eating behavior. The tendency to turn to food to cope with emotional states like stress, depression, anxiety, or boredom can persist. This weakens the effect of the surgery and can lead to weight regain.
- Snacking Habit: Continuous and uncontrolled snacking throughout the day can significantly increase calorie intake. Even in small portions, frequent eating can prevent weight loss.
Physiological Causes
In some cases, failure may be related to the body’s response to the surgery.
- Stomach Dilation (Stomach Enlargement): The remaining part of the stomach after gastric sleeve surgery can expand over time due to poor eating habits. Eating large portions or consuming meals too quickly can stretch the remaining stomach section, causing it to regain its old flexibility. Stomach dilation allows the patient to eat more, which leads to weight gain.
- Metabolic Changes: The body may develop a defense mechanism against weight loss by slowing down its metabolism. This can lead to a plateau in weight loss. Changes in hormonal balance can also lead to increased appetite and make weight gain easier.
Technical Causes
Although rare, technical issues with the surgery itself can lead to failure.
- Inadequate Resection: If the stomach is not sufficiently reduced or is improperly shaped into a tube during the surgery, the patient’s appetite and portion control may not reach the expected level.
- Leakage or Other Complications: Complications that arise after surgery can hinder the patient’s recovery process and jeopardize long-term weight loss goals.

Solutions for Gastric Sleeve Failure
Failure after gastric sleeve surgery is not an endpoint but a turning point where the situation needs to be re-evaluated and a new roadmap defined. Various solutions can be pursued in this situation.
Behavioral and Medical Interventions
Non-surgical methods are usually the first choice of solution.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: It is essential for patients facing gastric sleeve failure to be re-evaluated by a team consisting of a bariatric surgeon, a dietitian, and a psychologist.
- Nutritional Counseling: A dietitian helps the patient re-examine their eating habits and create a more sustainable and healthy nutrition plan. Fundamental rules like avoiding liquid calories, getting enough protein and vitamins, and eating small, frequent meals are re-emphasized.
- Psychological Support: A psychologist or psychotherapist provides support to the patient in coping with eating disorders, emotional eating, or post-surgery adaptation issues. This is a critical step for long-term weight control.
- Physical Activity: A regular and appropriate exercise program can restart the weight loss process by boosting metabolism and increasing calorie burn.
Revision (Correction) Surgeries
In cases where behavioral and medical interventions are insufficient or the stomach has significantly dilated, revision surgeries may be considered. These surgeries are performed to correct or convert a previous bariatric surgery procedure. Revision surgery can be more complex and risky than the initial surgery, so it should be carefully planned by an experienced surgeon and a multidisciplinary team.
The most common types of revision surgeries are:
- Re-sleeve Gastrectomy: If the only cause of failure is stomach dilation, the stomach can be re-reduced to its previous size.
- Conversion of Gastric Sleeve to Gastric Bypass: This is the most common revision method. It is preferred for patients who have regained weight or are experiencing problems like severe acid reflux after gastric sleeve surgery. During the surgery, the stomach volume is further reduced, and a portion of the small intestine is bypassed to reduce nutrient absorption.
- Duodenal Switch: This type of revision is generally preferred for patients with a high body mass index (morbidly obese) or other metabolic diseases. This surgery both reduces the stomach and significantly restricts intestinal absorption.
Conclusion
Gastric sleeve surgery is a powerful tool in the fight against obesity, but it is not a standalone miracle. For a successful outcome, the surgical procedure must be combined with lifestyle changes, nutritional discipline, and psychological resilience. Experiencing a weight loss stall or weight regain after surgery can be disappointing, but it is not an end; it is a hurdle that can be overcome with the right steps.
What is important is to view this situation not as a failure but as an opportunity to identify the source of the problem and seek appropriate solutions. Seeking support from an expert team in this process is the most reliable way to achieve long-term success. Remember, this surgery offers you a chance for a new beginning, but progress on this new path depends entirely on your determination.