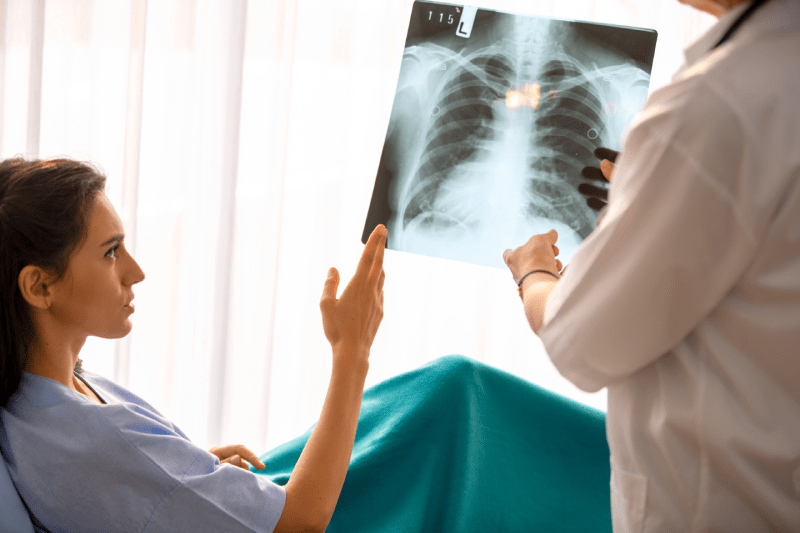
Lung cancer is a complex disease generally classified into two main types: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC). The biological behavior, rate of spread, and response to treatment of these two main types are completely different from each other. Due to these differences, the treatment for each patient must be meticulously personalized according to the tumor’s molecular characteristics and stage. Turkey is an important center offering these personalized treatments with advanced technology.
What Is The Fundamental Difference Between The Two Main Types Of Lung Cancer?
The two main types of lung cancer are Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC). The fundamental difference lies in the appearance of the cells under a microscope and their growth rates. NSCLC constitutes the majority of cases, spreads slower, and generally responds to surgery. SCLC is less common but grows very fast and metastasizes early; therefore, its treatment usually involves chemotherapy and radiotherapy instead of surgery. This biological distinction forms the starting point of the treatment strategy and significantly affects the prognosis of every patient.
What Is Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)?
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) is the more common type, representing approximately 80-85% of all lung cancer cases. It has subtypes such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. NSCLC tends to develop slower than SCLC, and when caught in the early stages, there is a high chance of complete cure with minimal invasive operations such as robotic surgery or VATS. In advanced stages, personalized smart drugs and immunotherapy based on molecular test results are the main methods for treating this type.
Why Is Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) Considered More Aggressive?
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) constitutes about 10-15% of cases but is considered extremely aggressive because it originates from neuroendocrine cells. Even at the time of diagnosis, this type tends to spread rapidly to other parts of the body, especially the brain and lymph nodes. Due to its fast growth rate, surgery is generally not a suitable option; instead, combinations of concurrent chemotherapy and radiotherapy are used to systematically target all cancer cells. Its aggressive nature makes SCLC a condition requiring emergency treatment.
How Is The Treatment Method Determined In Lung Cancer?
The treatment method is determined by a multidisciplinary council based on the cancer’s type (NSCLC/SCLC), stage (TNM system), and the patient’s general health status (performance status). Early stages of NSCLC are treated with surgery, while advanced stages are treated with immunotherapy or smart drugs based on molecular test results. SCLC is generally managed with systemic treatments (chemotherapy + radiotherapy). This personalized treatment decision is critical for maximizing treatment success and ensures the selection of the most appropriate approach.
What Is The Role Of Surgical Treatment For Early-Stage NSCLC?
Surgical treatment for Early-Stage NSCLC (Stage I and II) is the primary and most effective method offering a chance for cure. The purpose of surgery is to completely remove the cancerous tissue and nearby lymph nodes. Today, these operations are often performed using minimal invasive techniques like VATS (Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery) or Robotic Surgery. These techniques significantly improve the quality of treatment by providing less pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster patient recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
In Which Cases Are Smart Drugs Used In The Treatment Of NSCLC?
Smart drugs (targeted therapies) are used when specific genetic mutations (such as EGFR, ALK, ROS1) are detected in the tumor cells of NSCLC patients. Unlike chemotherapy, these drugs only attack these specific targets necessary for the growth and proliferation of cancer cells. Their side effects are generally fewer than chemotherapy, and they can yield very high response rates when used in the right patient. Therefore, molecular testing of the patient must be performed before starting treatment.
Is Immunotherapy Applied Differently In The Treatment Of NSCLC And SCLC?
Yes, the use of immunotherapy differs between NSCLC and SCLC. In NSCLC, immunotherapy (especially PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors) is frequently used as the first option, often in combination with chemotherapy or alone, for the treatment of metastatic (Stage 4) disease. In SCLC, the role of immunotherapy is more complex and is not yet as common a standard treatment option as in NSCLC. However, current clinical studies continue to investigate the potential benefits of immunotherapy in SCLC as well.
Which Method Forms The Basis Of SCLC Treatment?
Since Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) generally spreads rapidly, the basis of treatment is systemic therapy, meaning chemotherapy. Even when caught in the early stages, chemotherapy is usually applied concurrently with radiotherapy (chemoradiotherapy) to achieve local control. This combined approach aims to increase treatment efficacy by targeting both the local tumor and the rapidly spreading microscopic metastases. Surgery is a rare option considered only in very early and limited circumstances.
What Is Applied To Patients Not Suitable For Surgery For Early-Stage NSCLC?
Patients diagnosed with early-stage NSCLC but not suitable for surgery due to advanced age, severe heart, or lung diseases are treated with SBRT (Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy), which provides local control equivalent to surgery. SBRT involves delivering a very high dose of radiation to the tumor in a short period, typically 1 to 5 sessions, with millimetric precision. This method offers high success rates by allowing the patient to avoid the stress of surgery and recover quickly.

How Do Molecular Tests Affect The Cost And Duration Of Treatment?
Molecular tests (EGFR, ALK, PD-L1 analysis) initially require a cost and time investment, but in the long run, they reduce treatment costs and optimize the treatment duration. The correct test ensures the patient avoids expensive and ineffective chemotherapy, accelerating their transition to smart drugs with high response rates. This increases treatment success while preventing unnecessary and high-side-effect treatments, which positively affects the patient’s quality of life and total treatment budget.
How Are NSCLC Subtypes Adenocarcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma Distinguished?
NSCLC subtypes Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma are distinguished by their microscopic appearance, as well as the genetic mutation profiles they typically possess. Adenocarcinoma is generally more common in non-smokers and often carries targetable mutations like EGFR or ALK, making it suitable for smart drug treatment. Squamous cell carcinoma is more associated with smoking and carries fewer targetable mutations; its treatment usually involves combinations of chemotherapy and immunotherapy.
Why Is The Risk Of Brain Metastasis High In SCLC Patients?
The risk of brain metastasis is high in SCLC patients due to the neuroendocrine cell structure and rapid spreading (aggressive) tendency of this cancer type. SCLC cells can establish themselves in distant organs like the brain at an early stage via the bloodstream. Therefore, administering prophylactic cranial irradiation (preventive brain radiotherapy) to patients diagnosed with SCLC has become a standard approach. Early detection and treatment of brain metastases directly affect the patient’s lifespan and quality of life.
Why Should The PD-L1 Test Be Performed Before Starting Immunotherapy?
Performing the PD-L1 (Programmed Death Ligand 1) test before starting immunotherapy is critical for predicting the success of the treatment. This test measures the density of the PD-L1 protein on the surface of tumor cells. Tumors with high PD-L1 levels tend to respond better to immunotherapy as they are prone to blocking the immune system. The result of this test supports the oncologist’s decision on whether to apply immunotherapy alone or in combination with chemotherapy.
Why Is Chemotherapy Given After Surgical Treatment For Lung Cancer?
The main purpose of giving chemotherapy after surgical treatment for lung cancer (adjuvant chemotherapy) is to reduce the risk of recurrence by destroying microscopic cancer cells that may have remained in the body. Adjuvant therapy is standard in patients with lymph node involvement (Stage II and III) to support surgical success. This additional systemic treatment significantly increases the patient’s long-term survival chance by lowering the probability of cancer return.
What Methods Are Used When Resistance Develops In NSCLC Treatment?
When resistance develops in NSCLC treatment (especially to smart drugs), the treatment strategy is re-evaluated. The first step is to analyze new genetic mutations in the tumor with a new biopsy or liquid biopsy. Based on these analysis results, a switch to second or third-generation smart drugs may be made, or chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of both may be added to the treatment. Understanding the resistance mechanisms is key to re-drawing the treatment roadmap.
Does The Role Of Radiotherapy In SCLC Treatment Differ In Early And Advanced Stages?
Yes, the role of radiotherapy in SCLC treatment differs according to the stage. In Limited Stage SCLC, radiotherapy is used curatively to target the tumor and regional lymph nodes concurrently with chemotherapy. In Extensive Stage SCLC, radiotherapy is generally palliative, meaning it aims to improve the patient’s quality of life by controlling symptoms such as brain metastases or bone pain. In both cases, radiotherapy plays a key role in treatment success.
Which Cancer Types Is Minimal Invasive Surgery (VATS) More Suitable For?
Minimal invasive surgical techniques such as VATS and Robotic Surgery are most suitable, especially for early-stage NSCLC (Stage I-II). Since these techniques are performed with small incisions, they significantly reduce the patient’s post-operative pain, shorten the hospital stay, and accelerate the return to normal activities. As SCLC is generally not suitable for surgery due to its widespread nature, these minimal invasive approaches are more standard and widely used in NSCLC treatment.
Why Is Performance Status Important In Choosing Lung Cancer Treatment?
The patient’s performance status (ECOG or Karnofsky score) indicates the extent to which the person can perform daily living activities and is a critical factor in deciding the intensity of the treatment. Patients with good performance status can receive standard treatments such as more intense chemotherapy, combined chemoradiotherapy, or surgery. In patients with poor performance status, lower doses or only palliative supportive treatments are preferred to minimize side effects and preserve quality of life.
What Is The Treatment For Rare Genetic Mutations In NSCLC?
Treatment for rare genetic mutations in NSCLC (e.g., MET, RET, HER2 mutations) is generally done with specially developed smart drugs (tyrosine kinase inhibitors). More comprehensive Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) tests are required to detect these rare mutations. Successful oncology centers can detect these rare mutations and provide a highly personalized treatment by offering rapid access to internationally approved drugs specific to the patient’s mutation.
Why Are Smart Drugs Not Widely Used In SCLC Treatment?
Smart drugs are not widely used in SCLC treatment because SCLC usually has multiple complex and heterogeneous genetic changes rather than a single targetable genetic mutation. This makes it difficult for a single smart drug to be effective against the tumor. The fast growth rate and tendency for early spread of SCLC prioritize systemic and broad-spectrum treatments such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
What Is The Effect Of New Generation Surgical Methods On Recovery Time In NSCLC Treatment?
New generation surgical methods like VATS and Robotic Surgery in NSCLC treatment dramatically shorten the patient’s recovery time compared to traditional open surgery. Small incisions mean less tissue damage, less blood loss, and less post-operative pain. Patients can usually return to their daily routines within 2-4 weeks, whereas full recovery after open surgery can take 2-3 months. This rapid recovery enhances the patient’s quality of life and compliance with treatment.
When Is The Combination Of Immunotherapy And Chemotherapy Preferred In Treatment?
The combination of immunotherapy and chemotherapy is generally preferred as the first-line treatment option in metastatic NSCLC patients who have low PD-L1 expression or do not have a genetic mutation (EGFR/ALK). The goal of this combination is to enhance the effectiveness of immunotherapy by having chemotherapy kill cancer cells and the released antigens activate the immune system. Clinical studies show that this combined approach provides higher and more durable responses compared to chemotherapy alone.
What Role Does Liquid Biopsy Play In The Diagnosis Of Lung Cancer?
Liquid biopsy plays an important role in the diagnosis and follow-up of lung cancer by analyzing circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) released into the blood from tumor cells. This method is used especially in cases where it is difficult to reach the tumor tissue or when it is necessary to non-invasively detect resistance mechanisms. Liquid biopsy can rapidly identify genetic mutations at the diagnosis stage and support treatment decisions by showing early recurrence of the disease during the treatment process.
What Is The Treatment Approach For Stage III Disease In NSCLC?
Stage III (locally advanced) disease in NSCLC means the tumor has spread to regional lymph nodes but not to distant organs. The treatment approach in this stage is usually multidisciplinary and combined. The standard treatment is generally concurrent chemoradiotherapy, and in some cases, the treatment success is attempted to be increased with immunotherapy consolidation following this combined therapy. Surgery may be considered only in selected cases where the tumor shrinks and becomes completely resectable after chemoradiotherapy.
Why Is Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation Performed In SCLC Treatment?
Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation (PCI), or preventive brain radiotherapy, is applied in SCLC treatment due to the tendency of SCLC to metastasize early and frequently to the brain. PCI aims to prevent or delay the settlement of cancer cells in the brain. PCI plays a vital role in protecting long-term survival and quality of life by reducing the risk of recurrence, especially in patients who respond well to treatment and whose disease is under control.
Do Radiotherapy Side Effects In Lung Cancer Differ According To Types?
Radiotherapy side effects differ depending on the size of the irradiated area, the radiation dose, and the technology used, rather than the type of cancer. However, since larger areas are generally treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy in SCLC, the risk of radiation pneumonitis (lung inflammation) may be higher. In NSCLC, side effects can be more local and minimal when more targeted techniques like SBRT are used. The treatment team makes special plans to minimize side effects.
How Is The Risk Of Relapse (Recurrence) Followed Up In Treated NSCLC Patients?
The risk of relapse in treated NSCLC patients is managed with a meticulous long-term follow-up program. This program generally includes physical examination, blood tests, and thorax/abdomen CT (tomography) imaging at intervals of 3-6 months for the first two years. Advanced imaging such as PET-CT or brain MRI may also be added depending on the patient’s smoking history and cancer stage. Early diagnosis is very important to increase the success of salvage therapy in relapsing patients.
How Are Respiratory Functions Affected After Lung Cancer Surgery?
Respiratory functions after lung cancer surgery can be affected to some extent depending on the amount of lung tissue removed. For example, it is normal to experience some shortness of breath after lobectomy (removal of one lobe). However, since the patient’s respiratory reserves (pulmonary function tests) are meticulously evaluated before surgery, the surgery is generally planned in a way that the remaining lung can sustain function. Regular pulmonary physiotherapy accelerates recovery.
Are The Side Effects Of Chemotherapy In SCLC Treatment More Severe Than In NSCLC?
The chemotherapy regimens used in SCLC treatment are generally more intense and are often applied concurrently with radiotherapy due to the aggressive nature of the cancer; therefore, the side effects can be more severe compared to the standalone chemotherapy for NSCLC. Especially a drop in blood cell counts (anemia, leukopenia) and the resulting risk of infection can be more pronounced. However, modern supportive treatments (anti-nausea drugs, blood cell growth factors) make these side effects manageable.
What Is The Role Of The Patient’s Smoking History In The Treatment Decision?
The patient’s smoking history plays an important role in the treatment decision, both in predicting the type of cancer and in predicting the response to treatment. Patients with a heavy smoking history are more likely to have SCLC or squamous cell NSCLC. Since smoking also suppresses the immune system and reduces the effectiveness of radiotherapy/chemotherapy, it is a vital factor that must be quit before starting treatment.
What Is The Goal Of Palliative Care In Advanced-Stage Lung Cancer?
The main goal of palliative care in advanced-stage lung cancer is to maximize the patient’s quality of life by controlling symptoms caused by the disease and its treatment. This care is applied concurrently with cancer treatment and covers services such as pain management, control of shortness of breath, management of nausea/vomiting, nutritional counseling, and psychological support. Palliative care allows the patient to undergo a more comfortable treatment process, boosting morale.
When Is Liquid Biopsy Preferred For Genetic Analysis In NSCLC Treatment?
Liquid biopsy is preferred for genetic analysis in NSCLC treatment, especially in cases where sufficient tumor tissue cannot be obtained or in patients who cannot undergo a tissue biopsy because surgical intervention is risky. It is also used to rapidly and non-invasively detect new mutations when resistance development to smart drugs is suspected during treatment. Liquid biopsy is a practical alternative that supports quick treatment decisions.
How Does Nutritional Support Differ In SCLC And NSCLC Treatment?
Nutritional support is important in both types, but SCLC patients may require more intensive support due to more aggressive treatments (concurrent chemoradiotherapy). SCLC treatments can increase side effects such as difficulty swallowing and loss of appetite. In NSCLC patients, specific nutritional adjustments are made for the side effects of smart drugs and immunotherapy. The goal in both cases is to ensure adequate protein and calorie intake to preserve muscle mass, strengthen immunity, and increase the patient’s overall treatment tolerance.

What Is The Effect Of High Technology On The Cost Of Cancer Treatment?
The use of high technology (robotic surgery, SBRT/VMAT, PET-CT) in cancer treatment increases the cost; however, these technologies reduce the cost in the long run by reducing side effects and lowering the risk of recurrence. Turkey offers these advanced technologies at more competitive prices compared to Western countries. This allows patients to access the most current methods with economic advantages without compromising treatment quality, thereby increasing the overall effectiveness of the treatment.
What Is Done To Prevent Recurrence After Surgery In NSCLC?
Adjuvant (supportive) treatments are generally applied to prevent recurrence after surgery in NSCLC. This can be done with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or new-generation smart drugs, depending on the tumor’s stage and genetic features. For instance, in some NSCLC types, the use of targeted smart drugs for one year after surgery significantly reduces the risk of recurrence. The patient’s diligent adherence to the regular follow-up program and quitting smoking are key roles in this process.
What Advantages Do Oncology Centers In Turkey Offer In The Treatment of NSCLC And SCLC?
Oncology centers in Turkey offer significant advantages to international patients in the treatment of NSCLC and SCLC. These advantages include high service quality secured by JCI accreditation, fast diagnosis and treatment initiation times, rapid access to the latest immunotherapy and smart drugs, and these services being offered at 50-70% more affordable costs compared to the West. Patients also benefit from health tourism services such as medical translation and logistical support throughout their treatment process.
Are Drug Side Effects Less In NSCLC Treatment Compared To SCLC?
When smart drugs and immunotherapy are used in NSCLC treatment, the side effects are generally fewer and more manageable compared to the traditional and intense chemotherapy used in SCLC treatment. Smart drugs cause less damage to healthy cells because they only target cancer cells. Although immunotherapy has its own autoimmune side effects, it generally does not cause the classic side effects of chemotherapy such as nausea, vomiting, and hair loss.
How Is Psychological Support Provided On The Treatment Journey For Lung Cancer?
Psychological support on the challenging treatment journey for lung cancer is critical for the patient to maintain their quality of life and compliance with treatment. Oncology centers help patients and their families cope with emotional difficulties such as anxiety, depression, and fear through psycho-oncology specialists. Individual counseling and support groups enable the patient to feel psychologically strong in their cancer journey, boosting morale for the recovery process.
In Which Lung Cancer Types Can Immunotherapy Treatment Be Used For A Longer Period?
Immunotherapy treatment can generally be used for a longer period (up to 2 years in some protocols) and effectively in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) types. In SCLC, the long-term use of immunotherapy is still a subject of clinical research. NSCLC patients, when they respond well to treatment and do not develop severe side effects, can continue to receive immunotherapy for an extended period to continue supporting the immune system and maintaining control over the disease.
What Center Criteria Should Be Looked At For The Best Result In Cancer Treatment?
For the best result in cancer treatment, the center selection should focus on whether the center has international JCI accreditation, whether the multidisciplinary tumor council meets routinely, whether it has advanced technologies like robotic surgery and SBRT/VMAT, and whether it has high case volume and experience in the relevant cancer type (e.g., lung). These criteria guarantee a personalized and effective treatment.
Why Should Turkey Be Considered For Lung Cancer Treatment?
Turkey should be considered for lung cancer treatment because it is a strong alternative due to its application of international standard advanced technology (VATS, SBRT) and the latest treatment protocols (immunotherapy, smart drugs). Turkey offers the opportunity for treatment at much more affordable costs compared to the West while eliminating long waiting times, ensuring treatment can start immediately. This economic and rapid access advantage plays a significant role in increasing the patient’s chance of survival.
The lung cancer treatment journey is complex and requires personalized and current treatment appropriate for the type and molecular structure of your disease.
To confidently manage this challenging process with a high-technology treatment plan prepared by expert multidisciplinary teams in Turkey and benefit from comfortable health tourism services, you can contact Cure Holiday. We are happy to be by your side on your personalized treatment journey.