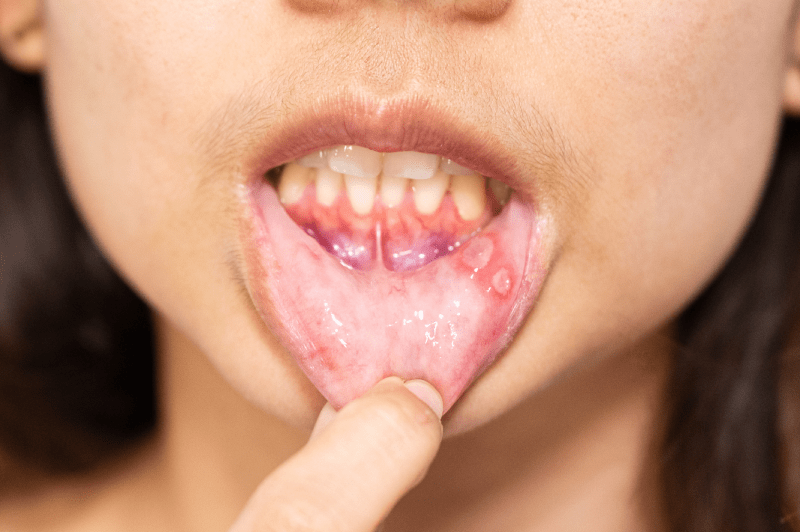
What is Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the areas that make up the oral cavity, such as the lips, tongue, inner surface of the cheeks, palate, gums, and floor of the mouth. Most oral cancers are a type known as squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer cells grow uncontrollably, forming masses called tumors, and can spread to surrounding tissues. When detected early, it is a type of cancer that is easier to treat and has a higher success rate. Therefore, regular dental check-ups and being vigilant about suspicious changes in the mouth are of vital importance.
What are the Main Symptoms of Oral Cancer?
The symptoms of oral cancer can sometimes be mistaken for other oral diseases. The most common symptoms include non-healing sores on the mouth or lip that last longer than 2 weeks, white or red patches, a feeling of numbness in the mouth, difficulty chewing or swallowing, a feeling of something stuck in the throat, swelling in the neck, and changes in voice. These symptoms do not always mean cancer, but if they persist for more than 2 weeks, it is necessary to consult a dentist or an ear, nose, and throat specialist.
What are the Main Causes of Oral Cancer?
The main risk factors for oral cancer include the use of tobacco products such as cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and excessive alcohol consumption. When these two factors come together, the risk increases significantly. Additionally, human papillomavirus (HPV) infections, excessive exposure to sunlight (ultraviolet light) (especially for lip cancer), poor nutrition, and poor oral hygiene are also among the risk factors.
How is Oral Cancer Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of oral cancer usually begins with a comprehensive examination by a dentist or an ear, nose, and throat specialist. The doctor checks for suspicious lesions or masses inside the mouth. For a definitive diagnosis, a small tissue sample called a biopsy is taken from the suspicious area and examined in a pathology laboratory. If necessary, imaging tests such as MRI, CT, or PET are used to determine the spread and stage of the cancer.
Is Oral Cancer Contagious?
No, oral cancer is not a contagious disease. Cancer cells do not pass from one person to another through coughing, sneezing, or touch. However, some types of oral cancer may be associated with human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted virus. While this virus is contagious, the cancer itself is not. Therefore, close contact with a person who has oral cancer or using their belongings does not pose a risk.
How is Oral Cancer Treated?
The treatment for oral cancer varies depending on the type and stage of the cancer and the patient’s overall health. A multidisciplinary approach, where more than one treatment method is used, is generally adopted. The main treatment methods include surgery (removal of the tumor), radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. In advanced stages, new treatment methods such as targeted therapy or immunotherapy may also be applied.
What are the Side Effects of Oral Cancer Treatment?
The side effects of oral cancer treatment vary depending on the treatment method applied. After surgery, limited mouth movement, swelling, or numbness may be observed. Radiation therapy can cause dry mouth, changes in taste, difficulty swallowing, and tooth decay. Chemotherapy can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and a weakened immune system. Supportive treatments are applied to manage these side effects.
Does Oral Cancer Recur After Treatment?
There is a risk of oral cancer recurrence after treatment. This risk depends on the stage at which the cancer was first diagnosed, the size of the tumor, and its spread. The likelihood of recurrence is lower in cancers treated in early stages. To reduce the risk of recurrence, it is very important for patients to have regular follow-up appointments after treatment, to stay away from risk factors such as smoking and alcohol, and to adopt a healthy lifestyle.
What is the Survival Rate of Oral Cancer?
The survival rate for oral cancer varies greatly depending on the stage at which the cancer is diagnosed. The 5-year survival rate for oral cancer diagnosed in early stages (Stage I and II) is over 80%. However, this rate decreases when the cancer is diagnosed at a more advanced stage and has spread to lymph nodes or distant organs. Early diagnosis and modern treatment methods increase the quality of life and longevity of patients.
Do Tobacco Products Cause Oral Cancer?
Yes, tobacco products are one of the biggest causes of oral cancer. Cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and smokeless tobacco products contain chemicals that damage cells in the mouth and lead to cancer development. Tobacco use increases the risk of cancer in all areas of the oral cavity, including the lips, tongue, gums, and floor of the mouth. Quitting tobacco products significantly reduces the risk of oral cancer.
Does Alcohol Consumption Cause Oral Cancer?
Yes, excessive and regular alcohol consumption increases the risk of oral cancer. Alcohol can damage the DNA of cells in the mouth and enhance the carcinogenic effect of tobacco products. The combined use of tobacco and alcohol increases the risk of oral cancer many times over compared to their individual use. Therefore, limiting or completely quitting alcohol consumption is important for protecting against oral cancer.
What is the Role of the HPV Virus in Oral Cancer?
The human papillomavirus (HPV) is an important cause of oral cancers that develop particularly in the floor of the mouth and the back of the throat (oropharynx). Oral HPV infections can be transmitted sexually. Cancers caused by HPV generally behave differently from cancers associated with tobacco and alcohol and may have a better prognosis in some cases. The HPV vaccine can be protective against some types of oral cancer.
Do Sunspots on the Lips Turn into Cancer?
Excessive exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays is a significant risk factor for the development of lip cancer, especially on the lower lip. Chronic sun damage can cause precancerous lesions on the lip called solar keratosis. These spots can eventually turn into cancer called squamous cell carcinoma. Protecting the lips with lip balms that contain sunscreen reduces this risk.
Are White or Red Patches in the Mouth Cancer?
White patches in the mouth are called leukoplakia, and red patches are called erythroplakia. These lesions are not always cancerous but can be potentially precancerous. Especially erythroplakia carries a higher risk of cancer than leukoplakia. If such lesions do not heal, they must be examined with a biopsy to establish a definitive diagnosis.
What are the Stages of Oral Cancer?
The staging of oral cancer is based on the size of the cancer, whether it has spread to the lymph nodes, and whether it has metastasized to other parts of the body. Staging is numbered from 0 to IV. Stages I and II are considered early stages, while Stages III and IV are considered advanced stages. Staging plays a critical role in determining the treatment plan and predicting the course of the disease.
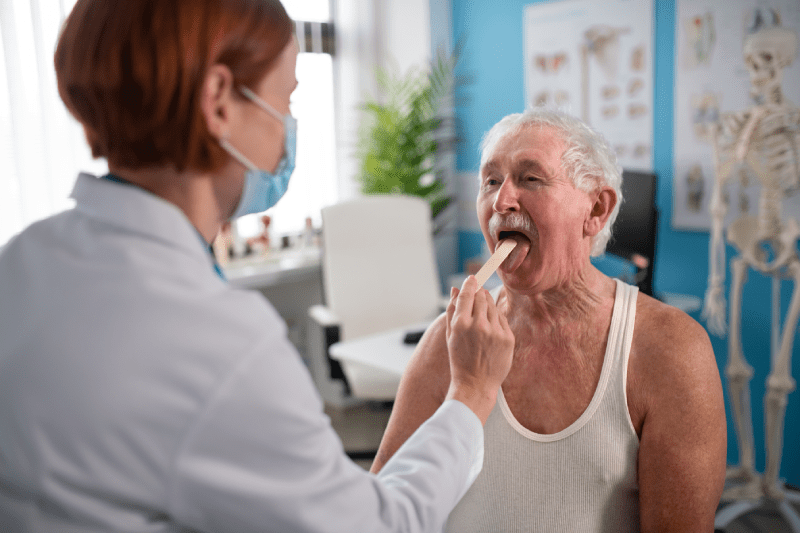
What are the Advanced Stage Symptoms of Oral Cancer?
In the advanced stages of oral cancer, tumors grow and become more prominent. Advanced stage symptoms can include persistent pain in the mouth or on the tongue, difficulty swallowing, weight loss, non-healing sores in the mouth, persistent swelling in the neck or jaw, loose teeth, hoarseness, and ear pain. These symptoms can be a sign that the cancer has spread to surrounding tissues or lymph nodes.
What is the Role of a Dentist in the Diagnosis of Oral Cancer?
Dentists play a critical role in the early diagnosis of oral cancer. During routine dental examinations, dentists can look for cancer or precancerous lesions inside the mouth. They carefully examine the oral mucosa, tongue, cheeks, and gums. When they detect a suspicious condition, they refer the patient to an ear, nose, and throat specialist for a biopsy. Therefore, regular dental check-ups are very important.
What is the Effect of Oral Health and Hygiene on Oral Cancer?
Poor oral hygiene and health can increase the risk of oral cancer. Chronic inflammation, irritation, and infections in the mouth can contribute to cancer development. Maintaining oral hygiene with regular brushing, flossing, and professional dental cleanings can help reduce the risk of oral cancer. At the same time, it allows for the early detection of suspicious changes in the mouth.
How is Oral Cancer Followed Up After Treatment?
After oral cancer treatment is completed, patients should continue to have regular doctor check-ups. This follow-up process is very important for checking whether the cancer has recurred and for managing side effects related to the treatment. Check-ups are more frequent in the first few years and then the intervals are extended over time. During these check-ups, the patient’s oral cavity, neck, and overall health status are evaluated.
How is Dry Mouth Related to Oral Cancer Treated?
Radiation therapy used in the treatment of oral cancer can damage the salivary glands and cause permanent dry mouth (xerostomia). This condition affects speech, swallowing, and the sense of taste. Artificial saliva products, special mouthwashes, and medications that increase saliva flow can be used for treatment. In addition, drinking plenty of water and avoiding sugary foods helps to relieve the symptoms.
Does Oral Cancer Occur in Children?
Oral cancer is generally seen in older adults and is rarely diagnosed in children. Oral cancers seen in children are usually associated with genetic syndromes or specific syndromes. However, with the increase in risk factors (tobacco, alcohol), its incidence is also increasing in young adults.
Can Symptoms on the Tongue Be Oral Cancer?
Yes, persistent sores, white or red patches, swellings, or hardened areas on the tongue can be symptoms of oral cancer. Lesions that appear on the side edges of the tongue and the floor of the mouth are considered more risky. Tongue cancer is one of the most common types of oral cancer, and its treatment can be successful when detected early.
What is Head and Neck Pain Related to Oral Cancer?
As oral cancer progresses, persistent pain in the head and neck may occur as a result of the tumor pressing on surrounding tissues and nerves. This pain is usually felt in the area where a non-healing sore is located and can radiate to the ears. Especially chronic, unexplained pain should be investigated as it may be a sign of cancer.
How is Surgical Treatment Applied in Oral Cancer?
Surgical treatment for oral cancer involves the removal of the tumor and the surrounding healthy tissue. The scope of the surgery varies depending on the size and location of the tumor. In some cases, lymph nodes may also be removed. After surgery, reconstructive surgery and physical therapy may be required for the patient to regain their functions (speech, swallowing).
What Can Be Done to Protect Against Oral Cancer?
The most effective way to protect against oral cancer is to stay away from risk factors. Quitting smoking and alcohol use, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, protecting from sunlight, and maintaining good oral hygiene are important. In addition, getting regular dental and medical check-ups to detect oral cancer early is of great importance.
What is the Place of Radiotherapy in the Treatment of Oral Cancer?
Radiotherapy is a treatment method that uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It can be used alone for early-stage tumors or after surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence. It is sometimes also used in combination with chemotherapy. Radiotherapy can cause side effects such as difficulty swallowing, dry mouth, and loss of taste, but modern techniques help reduce these side effects.
Do Nutritional Habits Affect the Risk of Oral Cancer?
Yes, nutritional habits affect the risk of oral cancer. A diet rich in fresh vegetables and fruits contains antioxidants that help reduce the risk of oral cancer. Poor nutrition weakens the body’s immune system and reduces its resistance to cancer. It is especially important to consume foods rich in vitamins A, C, and E.

Does Oral Cancer Have a Genetic Aspect?
Most cases of oral cancer develop due to environmental factors (tobacco and alcohol) rather than genetic predisposition. However, some rare genetic syndromes (e.g., Fanconi anemia) can increase the risk of oral cancer. People with a family history of oral cancer are advised to be more careful about risk factors and to have regular screenings.
What are the Symptoms of Cheek Cancer?
Cheek cancer is a type of cancer that begins on the inner surface of the cheeks. The most common symptoms include a non-healing sore on the inner surface of the cheek, white or red patches, pain or sensitivity, difficulty chewing, and swelling in the cheek. Smoking and alcohol use are important risk factors for cheek cancer.
What is the Multidisciplinary Approach in the Treatment of Oral Cancer?
The multidisciplinary approach in the treatment of oral cancer is when doctors from different specialties (surgeon, radiation oncologist, medical oncologist, dentist, speech therapist, dietitian) come together to create a personalized treatment plan for the patient. This approach aims to provide the best response to treatment and improve the patient’s quality of life.
What is the Earliest Symptom for Tongue Cancer?
The earliest symptom of tongue cancer is usually a non-healing, painless sore on the tongue that lasts longer than 2 weeks. This sore can grow over time and cause pain. White or red patches on the side edges or under the tongue are also early symptoms.
What are the Voice Changes Related to Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer can cause changes in the voice when it directly or indirectly affects the vocal cords. When a tumor restricts the movement of the tongue or the floor of the mouth, speech disorders can occur. Cancer that has spread to the lymph nodes in the neck can also cause hoarseness. Such voice changes should be consulted with a specialist, especially when they become chronic.
What Are Mouth Cancer Treatment Options In Turkey?
Patients with mouth cancer can choose from a variety of treatment options, including:
Surgery for oral cancer: The malignant cells, as well as some surrounding normal tissue or cells, are removed. The surgery’s scope is determined by the cancer’s size. If the cancer has progressed to other regions of the body, lymph nodes in the neck may also need to be removed. Mouth reconstruction is a type of surgery that some individuals may require following a cancer removal operation.
Reconstructive surgery is recommended to repair the mouth and allow the patient to speak and eat again. This procedure includes reconstructing the mouth with skin, muscle, or bone transplants from other areas of the body. The patient’s natural teeth may potentially be replaced with dental implants.
Radiotherapy for oral cancer involves delivering radiation beams to diseased tissue in order to destroy tumor cells.
Radiation treatment employs a variety of procedures and delivery systems.
Chemotherapy for oral cancer is the application of powerful anti-cancer drugs to destroy malignant cells. These may try to reduce the tumor, stop it from developing, or remove cancer from the body as a whole.
These treatments are frequently used in combination. After the operation, a course of radiation or chemotherapy for oral cancer may be performed to help prevent the cancer from returning.
What Is The Cost Of Oral Cancer Treatment In Turkey?
This will be determined by the type of therapy, which is determined by a number of criteria including the patient’s age, overall health, and the stage, location, and type of oral cancer. Also, the complications, reputation of the hospital and success rate of treatments affect the cost of mouth cancer treatment in Turkey.
Turkey is a popular destination for sophisticated medical treatment, particularly for complicated illnesses like cancer. The country has the greatest hospitals in the world, complete with cutting-edge technology and globally educated physicians with extensive expertise.
Patients from all over the globe come to Turkey’s certified and famous hospitals for high-quality medical services. These hospitals provide inexpensive packages that include a variety of services and amenities.
Recovery After Oral Cancer Treatment In Turkey
The length of your recovery following oral cancer treatment in Turkey is determined on the treatments you underwent. If you’ve had surgery, you’ll almost certainly have a drip in your arm feeding you fluids until you’re able to eat on your own. You’ll probably have a wound drain and a catheter in place to collect and measure pee as well.
You’ll have a breathing tube in your neck if you’ve undergone a tracheotomy.
Following oral cancer therapy, it might be difficult to speak after the procedure. This might be frustrating at times. As a result, having someone nearby to take care of things for you and comprehend what you may need to say is critical. It is common to experience pain following surgery for a few days and it can be overcome with medication.
Can I Find Professional Oral Cancer Surgeons In Turkey?
Oral cancer treatment surgeons in Turkey are known across the world for their competence and understanding. They collaborate with a team of doctors and nurses to give comprehensive and effective therapy to their patients and to provide the best Oral Cancer Treatment in Turkey. Turkey’s oral cancer surgeons are highly skilled and trained, having degrees from prestigious national and international universities. They give the greatest clinical services to each and every patient, including medical and surgical intervention based on their diagnosis.
These surgeons are well-versed in the use of cutting-edge technology and the most up-to-date procedures in Oral Cancer Treatment. Many of these surgeons have additional specialities or sub-specializations in the field of Oral Cancer Treatment, and they provide exact treatment for the patient’s condition. Turkey’s experienced surgeons for cancer seek to improve the healthcare in the country.
Is Turkey Good For Oral Cancer Treatment?
Turkey is considered as one of the top countries for mouth cancer treatment and other medical treatments. Oral Cancer Treatment is provided by Turkish specialists who have many years of expertise. They hold medical degrees from prestigious universities and have worked at Turkey’s leading hospitals. The surgeons use the most up-to-date medical and surgical technology to provide exceptional care to their patients. They are also known across the world for their expertise and skills, as patients from all over the world come to them for mouth cancer treatment in Turkey. They are also members a number of national and international medical associations.
Why Travel To Turkey For Onchology Treatment?
Apart from the top surgeons in Turkey for onchology, people come to this country for medical care for a variety of reasons, including cost-cutting without sacrificing quality, access to modern medical equipment, and hospital standards that are world-class. For international patients, the hospitals provide a complete package, making treatment in Turkey highly cost-effective and allowing them to save a significant amount of money.


