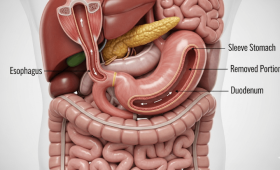
What is Gastric Sleeve Surgery and How is it Performed?
Gastric sleeve surgery is one of the most common surgical methods used in the treatment of obesity. This procedure involves the surgical removal of approximately 80% of the stomach, leaving the stomach in the shape of a banana or a tube. The surgery is performed laparoscopically (minimally invasive), which means a few small incisions are made in the abdomen instead of a large one. The surgeon enters through these incisions with special tools to cut and remove the greater curvature of the stomach. The remaining part is closed with a suture line. The main goal of the surgery is to help the patient feel full with less food and to create hormonal changes by removing the part of the stomach where the hunger hormone (ghrelin) is produced. This way, the patient starts losing weight by eating less.
What is Gastric Botox and How is it Applied?
Gastric Botox is a non-surgical method for obesity treatment. During the procedure, an endoscope is used to enter the stomach, and botulinum toxin (Botox) is injected into the stomach muscles, particularly in specific active areas. These injections temporarily weaken the muscle’s ability to contract and delay stomach emptying. When the stomach stays full for a longer period, it helps the patient feel less hungry and full with less food. The procedure takes about 15-20 minutes and is usually performed under sedation. Since gastric Botox is not a surgical procedure, it does not leave incisions, sutures, or scars, and does not require hospitalization.
Which Patients are Suitable for Gastric Sleeve and Which are Candidates for Gastric Botox?
Gastric sleeve surgery is generally suitable for morbidly obese patients with a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 40 and above, or for those with a BMI between 35−40 who have obesity-related co-morbidities such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnea. This surgery is ideal for cases requiring significant and permanent weight loss. Gastric Botox, on the other hand, can be an option for individuals with a milder weight excess, with a BMI between 27−35. It is a more suitable alternative for people who do not want to undergo surgery, struggle with diet and exercise, or do not want to take a serious surgical risk. Patients with stomach issues like ulcers, gastritis, or those allergic to Botox are not candidates for gastric Botox.
What is the Main Goal of Both Methods?
The main goal of both gastric sleeve surgery and gastric Botox is to achieve weight loss by limiting the patient’s calorie intake. However, the objectives of these two methods are slightly different. Gastric Botox is generally seen as a “kick-start” or “supportive” method to a diet and exercise program, aiming to assist with weight loss rather than treating obesity itself. Gastric sleeve surgery is a permanent surgical intervention aimed at treating morbid obesity. This operation aims to control obesity by fundamentally changing the patient’s eating habits and creating hormonal adjustments.
What are the Most Distinct Differences?
The most distinct difference between gastric sleeve surgery and gastric Botox is that one is a surgical procedure and the other is non-surgical. Sleeve gastrectomy is a permanent and irreversible operation where a part of the stomach is removed. Gastric Botox, however, is a temporary procedure, and its effect wears off after a certain period. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia and requires hospitalization. Gastric Botox is performed with sedation, endoscopically, and does not require hospitalization. While the results of the surgery are permanent and more pronounced, the effect of Botox is temporary, and its weight loss potential is lower compared to surgery.
What is the Weight Loss Potential and Efficacy of Each Method?
Gastric sleeve surgery helps patients lose an average of %60-%80 of their excess weight, and this weight loss is generally permanent. The high success rate of the surgery is due to both physical (reduced stomach volume) and hormonal (decreased hunger hormone) effects. Gastric Botox helps patients lose an average of %10-%20 of their excess weight. Botox is a better option for patients with mild weight excess or those who do not want to undergo surgery. Its effectiveness depends on the patient’s adherence to a diet and exercise program and is lower compared to gastric sleeve surgery.
What are the Differences in Recovery Times?
The recovery period after gastric sleeve surgery is longer. Patients typically stay in the hospital for 2−3 days after the operation, and full recovery can take several weeks. A specific nutrition plan is followed, starting with a liquid diet for the first few days, gradually moving to pureed and solid foods. After gastric Botox, the recovery period is almost non-existent. The patient can return to their daily routine immediately after the procedure. Mild stomach discomfort or bloating may occur after the procedure, but these symptoms resolve quickly.
While Gastric Sleeve Surgery Offers a Permanent Solution, How Long Does the Effect of Gastric Botox Last?
Gastric sleeve surgery is a permanent solution due to the reduction of the stomach and the removal of the area where the hunger hormone is secreted. Patients must adhere to lifelong dietary and lifestyle changes. The effect of gastric Botox is temporary and generally lasts for about 4−6 months. After this period, as the effect of Botox diminishes, the stomach muscles regain their original contractile strength, and the patient can revert to old eating habits. Therefore, adherence to diet and lifestyle changes after the Botox procedure is crucial for a successful outcome.
What are the Risks and Possible Side Effects of Both Methods?
Gastric sleeve surgery, like any surgical procedure, carries certain risks. These risks include bleeding, infection, complications related to anesthesia, and the risk of a leak from the stomach staple line. In the long term, conditions such as vitamin and mineral deficiencies, reflux, or hiatal hernia may occur. Gastric Botox carries much fewer risks. The most common side effects are mild nausea, bloating, or abdominal pain after the procedure. These side effects are usually short-lived. Serious side effects, such as the botulinum toxin entering the systemic circulation, are extremely rare.
Which Method is More Economical for Patients?
Gastric Botox is more economical than gastric sleeve surgery as it is a non-surgical procedure. Since gastric Botox does not involve hospitalization, operating room costs, and the fees of a surgical team, the total cost is significantly lower. Gastric sleeve surgery, being a surgical operation, is more expensive due to costs for anesthesia, hospital stay, operating room use, and surgical materials. However, it should be noted that since the effect of gastric Botox is temporary, it may need to be repeated at certain intervals, which can increase the long-term cost.
What are the Dietary and Lifestyle Changes After Gastric Sleeve Surgery?
The diet after sleeve gastrectomy changes gradually. For the first few weeks after the surgery, patients are on a clear liquid diet, followed by pureed foods. After about a month, solid foods are slowly added to the menu. Patients must eat small, frequent meals, chew their food well, and avoid drinking liquids during or immediately before meals. Lifestyle changes include regular exercise, drinking plenty of water, and taking vitamin supplements. These changes are vital for permanent weight loss and a healthy life.
What Should the Diet be After Gastric Botox?
The diet after gastric Botox is more flexible than after sleeve gastrectomy, but it still requires discipline. The effect of the procedure reduces the patient’s appetite, so they feel less hungry and get full sooner. This makes it easier for the patient to follow a healthy diet plan and control portion sizes. Patients are advised to consume high-fiber foods, avoid processed and sugary foods, and drink enough water after the procedure. Avoiding hard-to-digest foods can be beneficial as stomach emptying time is prolonged. The most important thing is to use the effect of Botox to adopt healthy eating habits with the guidance of a dietitian.
What are the Long-Term Success Rates of Both Methods?
The long-term success rate of gastric sleeve surgery is very high. Most patients maintain a significant portion of their weight loss within 5 years after the surgery. Weight regain, though rare, can occur, usually when lifestyle changes are not maintained. The long-term success of gastric Botox depends on the patient’s ability to maintain the healthy eating habits they acquired after the effect of the Botox wears off. If the patient returns to their old eating habits, the weight lost with the help of Botox can be quickly regained. Therefore, the success of Botox is more dependent on the patient’s own efforts.
What is the Weight Loss Mechanism of Gastric Botox?
The weight loss mechanism of gastric Botox is based on temporarily slowing down the movement of the stomach muscles. When Botox is injected, the stomach’s muscle contraction power decreases, which prolongs the stomach emptying time. Since food stays in the stomach longer, the satiety signals sent to the brain increase, and the patient feels full for a longer period while eating less. Additionally, some studies suggest that Botox may also affect hormones that regulate appetite, but the main mechanism is the slowing of stomach emptying. This effect helps the patient naturally limit their calorie intake.
What Hormonal Changes Does Gastric Sleeve Surgery Cause in the Body?
Gastric sleeve surgery not only reduces the stomach’s volume but also causes significant hormonal changes. The part of the stomach that is removed during the surgery is the main production center for the hunger hormone, ghrelin. The removal of this hormone causes a significant decrease in the patient’s appetite after the surgery. Furthermore, sleeve gastrectomy also positively affects the secretion of intestinal hormones like GLP-1, which increases insulin sensitivity and can improve diabetes. These hormonal changes enhance the surgery’s effectiveness on weight loss and metabolic diseases.
How Does Gastric Botox Affect Stomach Movements?
Gastric Botox works by slowing down stomach movements. The stomach contracts to start the digestion process and push food into the small intestine. Botulinum toxin blocks the nerve signals that cause these contractions. As a result, the stomach muscles contract less and more slowly, which leads to a prolonged stomach emptying time. Since food remains in the stomach for a longer period, the patient experiences a longer-lasting feeling of fullness, which helps in reducing calorie intake.
Are Both Methods Suitable for Patients with Co-morbidities?
Gastric sleeve surgery is a frequently recommended treatment for patients with co-morbidities such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and metabolic syndrome related to morbid obesity. The surgery provides a significant improvement in the symptoms of these diseases and can even allow some patients to stop taking medication. Gastric Botox can help manage these co-morbidities in patients who cannot undergo surgery or do not meet the criteria, but it does not offer as strong and permanent an effect as sleeve gastrectomy. Gastric Botox contributes to the indirect control of these diseases by aiding weight loss.
How is the Patient’s Psychological State Affected After the Procedure?
Both methods can positively affect the patient’s psychological state. Weight loss can boost an individual’s self-confidence, improve their social interactions, and enhance their overall quality of life. However, a radical change like sleeve gastrectomy can lead to psychological challenges for some patients due to the severe restrictions on eating habits. Therefore, it is crucial to seek psychological support before and after the surgery. Gastric Botox places less psychological burden than surgery, but it can lead to disappointment if the expected weight loss is not achieved.
Is Gastric Botox Sufficient as a Standalone Weight Loss Method, or Should it be Combined with a Diet and Exercise Program?
Gastric Botox is not a sufficient weight loss method on its own. The injection itself only reduces appetite and slows down stomach emptying, but for permanent weight loss, the patient must use this effect to adopt healthy eating and regular exercise habits. Gastric Botox offers the patient an “opportunity” to transition to a healthy lifestyle. Therefore, the procedure must be planned and implemented with a dietitian and an exercise specialist. Relying solely on Botox will prevent lasting success and lead to weight regain.

How Does Gastric Sleeve Surgery Reduce the Risk of Obesity Recurrence?
Gastric sleeve surgery reduces the risk of obesity recurrence both physically and hormonally. Since the stomach’s volume is permanently reduced, the patient can physically eat less food. Additionally, the decrease in the production of the hunger hormone ghrelin makes it easier for the patient to control their appetite. These two main mechanisms lead to a permanent change in eating habits, which minimizes the risk of obesity returning. However, if the patient reverts to unhealthy food choices and a sedentary lifestyle after surgery, weight regain can occur.
How Often Can the Gastric Botox Procedure be Repeated?
Since the effect of the gastric Botox procedure is temporary, it can be repeated if the patient does not meet their weight loss goals or to maintain the weight they have lost. Gastric Botox can usually be repeated every 4−6 months. Specialists generally determine this period based on the patient’s needs. However, even after the Botox procedure is repeated several times, it is essential for the patient to adhere to lifestyle changes supported by diet and exercise and to adopt permanent habits.
What Preparations Should Patients Make Before the Surgery or Procedure?
Before gastric sleeve surgery, patients undergo a comprehensive evaluation. This evaluation includes endoscopy, blood tests, and psychiatric and endocrinological examinations. Patients must quit smoking and follow the diet plan recommended by their doctor before the surgery. The preparation process before gastric Botox is shorter. The stomach only needs to be empty before the procedure, so the patient must fast for about 8 hours.
What are the Potential Complications of Both Methods and How are They Managed?
The most serious complication of sleeve gastrectomy is a leak from the staple line. This condition may require emergency surgical intervention and long-term antibiotic treatment. Other complications include infection, bleeding, and blood clots. These complications can be managed with the surgeon’s experience and careful post-operative follow-up. In gastric Botox, serious complications are very rare. The most common issues are mild nausea or cramps, which usually resolve on their own. If the Botox is injected incorrectly, an excessive slowing of stomach movements may occur, which can be treated with medication.
How Does Gastric Sleeve Surgery Permanently Change Patients’ Eating Habits?
Gastric sleeve surgery fundamentally changes patients’ eating habits. As the stomach volume is reduced, patients get full with smaller portions, and it becomes impossible for them to eat large meals. The patient is forced to adopt the habit of eating small, frequent meals. Furthermore, some types of food and drinks (e.g., carbonated beverages, sugary foods) can cause discomfort, which helps patients stay away from them. These changes provide the foundation for the patient to adopt and maintain a healthy diet.
How Does Gastric Botox Affect and Reduce Patients’ Appetite?
Gastric Botox works by reducing patients’ appetite. The prolonged stomach emptying time sends a constant satiety signal to the brain. This makes the patient feel less hungry and consume less food. The degree of appetite reduction varies from person to person, but in general, patients feel a significant decrease in appetite in the first few weeks after the procedure. The effect of Botox on appetite continues as long as the patient adheres to their diet and prefers healthy foods. However, this effect is not permanent like in sleeve gastrectomy.
Based on What Criteria Should a Patient Choose Between Gastric Sleeve Surgery and Gastric Botox?
When choosing between gastric sleeve surgery and gastric Botox, a patient should first consider their BMI and overall health. Gastric sleeve surgery is a more suitable option for patients with a BMI over 35 and serious obesity-related co-morbidities. For patients with a milder weight excess, who do not want to undergo surgery, or who cannot tolerate surgical risks, gastric Botox can be a good starting point. The patient’s lifestyle, eating habits, and weight loss goals also play a role in this decision. For both methods, it is best to make the final decision after a detailed evaluation with a bariatric surgeon and a dietitian.
For which BMI (Body Mass Index) range of patients is gastric sleeve surgery the most suitable option?
Gastric sleeve surgery is generally considered the most suitable option for patients with a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 40 or higher. Patients in this group are referred to as “morbidly obese.” Additionally, it is highly recommended for individuals with a BMI between 35 and 39.9 who have comorbidities related to obesity, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, or high cholesterol. The potential for this surgery to improve obesity-related health problems and enhance the quality of life for patients within this range is high. However, BMI alone is not sufficient for the surgery decision. The patient’s overall health, lifestyle, eating habits, and psychological state are also evaluated in detail to create a personalized treatment plan. This holistic approach is vital for ensuring the long-term success of the surgery.
What is the most important advantage of sleeve gastrectomy over other surgical methods?
The most important advantage of sleeve gastrectomy over other bariatric surgical methods (e.g., gastric bypass) is that it does not significantly alter the anatomy of the digestive system and does not involve an intestinal bypass. This means that post-operative vitamin and mineral absorption disorders are less common. While malabsorptive operations like gastric bypass may require patients to take vitamin supplements more frequently for life, this risk is lower with sleeve gastrectomy. Additionally, being a technically simpler procedure, the shorter operation time and the corresponding reduction in post-operative complications are significant advantages. The mere reduction in stomach volume allows the natural course of digestion and absorption functions to be preserved, which helps the patient lose weight in a healthier and more balanced way.
How does the reduction in stomach volume after surgery permanently change the patient’s eating habits?
The reduction in stomach volume after surgery fundamentally and permanently changes the patient’s eating habits. Since approximately 75-85% of the stomach is removed, patients begin to feel full with a very small amount of food. This physical restriction automatically encourages the patient to control their portions and eat less. Patients must adhere to new dietary rules after surgery, which involves a phased diet plan including a transition from liquids to purees and finally to solid foods. This process reinforces the habit of choosing more nutritious and protein-rich foods over high-calorie snacks. The biological and physical restrictions imposed by the surgery provide a strong foundation for patients to adopt healthy eating habits and ensure their sustainability in the long run.
How does gastric sleeve surgery affect the levels of the hunger hormone ghrelin, and what is its contribution to the weight loss process?
Gastric sleeve surgery contributes to the weight loss process both mechanically and hormonally. During the surgery, the fundus, the part of the stomach where most of the hunger hormone known as ghrelin is produced, is removed. This operation leads to a significant decrease in circulating ghrelin levels. The reduction in ghrelin levels causes the patient’s hunger sensation to disappear or significantly diminish after surgery. This makes it much easier for the patient to control their calorie intake by reducing their appetite and desire to eat. As a result, patients lose weight not only due to the reduction in stomach volume but also with the help of a hormonal boost. This dual-mechanism effect makes gastric sleeve a more effective and permanent solution for weight loss compared to other methods.
Is sleeve gastrectomy a reversible procedure, and what are the risks for the patient?
Sleeve gastrectomy is an irreversible procedure. During the surgery, approximately 75-85% of the stomach is permanently removed and separated from the body. The biggest risk this poses to the patient is that the stomach cannot be returned to its original size if they are not satisfied with the results, experience insufficient weight loss, or require another surgery in the future. In rare cases, if problems such as insufficient weight loss or weight regain occur, revisional surgeries can be performed. For example, a sleeve gastrectomy can be converted into a gastric bypass. However, these revisional surgeries are more complex, longer, and carry higher risks of complications. Therefore, the decision to undergo sleeve gastrectomy is an important life choice that requires the patient to carefully consider their long-term goals and potential outcomes.
What are the potential long-term nutritional deficiencies (vitamin and mineral deficiencies) that may arise after surgery?
The most common long-term nutritional deficiencies that may arise after gastric sleeve surgery include deficiencies in vitamin B12, vitamin D, iron, folic acid, and calcium. Although the surgery does not impair absorption, patients may not be able to consume sufficient amounts of food due to the reduced stomach volume. This limits the intake of vitamins and minerals that should be obtained from food. Specifically, the “intrinsic factor” necessary for vitamin B12 absorption is produced in a part of the stomach, and its removal can lead to B12 deficiency. Therefore, patients who have undergone the surgery must use these supplements for life and have regular blood tests to monitor for deficiencies. Uncontrolled nutritional deficiencies can lead to serious health problems such as anemia, osteoporosis, or nervous system disorders.
What are the reasons for the increase in reflux disease after gastric sleeve surgery?
Some patients may experience an increase in reflux (gastroesophageal reflux disease) complaints after gastric sleeve surgery. The most common reason for this is the increased internal pressure on the stomach as it is shaped into a tube. Since the stomach cannot expand as it used to, its contents can be pushed back into the esophagus more easily. Additionally, the removal of the fundus during surgery can change the angle between the esophagus and the stomach (the Angle of His), which can also trigger reflux. This angle normally acts like a valve, preventing stomach contents from flowing back. In addition to this anatomical change, reflux complaints can be aggravated by not following the post-operative diet, especially by eating too quickly or consuming excessive amounts of liquid. This condition can be managed with lifestyle changes and medication prescribed by a doctor.
What are the most common surgical complications of the surgery, and what are the ways to reduce these risks?
The most common surgical complications of gastric sleeve surgery are leakage, bleeding, and infection. Leakage is a condition where stomach contents leak into the abdominal cavity from the staple line and is one of the most serious complications requiring immediate intervention. Bleeding can originate from the staple line or severed blood vessels and also requires intervention. An infection can develop in the surgical area or the abdominal cavity. To minimize these risks, choosing an experienced surgeon and team is critically important. All of the patient’s health checks must be meticulously performed before the surgery, and potential risks should be identified. In the post-operative period, the patient must strictly follow the instructions of the doctor and dietitian, especially by eating slowly and in small portions, paying attention to fluid intake, and avoiding heavy lifting, which significantly helps reduce these risks.
How does the ideal weight loss process for a patient who has undergone gastric sleeve surgery progress?
The ideal weight loss process for a patient who has undergone gastric sleeve surgery typically occurs most rapidly in the first 6 months. During this period, patients lose a large portion of their excess weight, and physical changes become most prominent. Weight loss usually continues for 12-18 months after the surgery, but the rate slows down and can enter a plateau phase. Ideally, patients can lose 60-70% of their excess weight within one year after surgery. This process is not solely a result of the surgical procedure but is also directly related to the patient’s ability to adapt to a regular exercise, healthy eating, and lifestyle changes. Surgery is merely a starting point, and lasting success depends on long-term lifestyle changes.
How can stomach enlargement after surgery and subsequent weight regain be prevented?
Stomach enlargement and weight regain after surgery are among the biggest long-term risks. To prevent this, the patient must make permanent lifestyle changes. Although the stomach is reduced in size through surgery, it can stretch over time. Portion control is of vital importance to prevent this stretching. Patients must maintain the habit of eating in small portions that they learned after the surgery. Additionally, it is crucial to stay away from high-calorie liquid foods (sugary drinks, creamy soups, desserts, etc.), as these can lead to high calorie intake without enlarging the stomach. Regular physical activity helps speed up the metabolism and prevents weight gain. Finally, regular follow-ups with a doctor and a dietitian help maintain the patient’s motivation and detect potential problems at an early stage.
What are the main benefits of gastric botox being a non-surgical procedure?
The most important benefit of gastric botox is that it is a non-surgical procedure. This means that the risks associated with surgery (incision, stitches, bleeding, infection) are completely eliminated. The procedure does not require general anesthesia, is performed endoscopically, and patients can usually return to their daily lives immediately after the procedure. The recovery period is almost zero, which provides great comfort and time savings for patients. Also, the effect of gastric botox is temporary, meaning the function of the stomach muscles returns to normal once the effect of the botox wears off. This makes it an ideal option for patients who do not want a permanent anatomical change or are not suitable for surgery. This procedure is an attractive alternative for people who have a fear of surgery or are looking for a milder solution.
What is the mechanism of action of gastric botox and how does it increase the feeling of fullness?
Gastric botox is administered by injecting botulinum toxin into specific points on the stomach wall using an endoscopic method. This toxin temporarily blocks the signals transmitted from the nerve endings to the muscles. As a result, the contraction ability of the stomach muscles weakens, and stomach emptying slows down. The longer food stays in the stomach, the more a continuous signal of fullness is sent to the brain. This allows the patient to feel full for a longer time with physically less food. It can also partially reduce the production of hunger hormones like ghrelin, but this effect is not as permanent and strong as that of gastric sleeve surgery. Gastric botox, with this mechanism, helps control appetite and supports the weight loss process by enabling the patient to consume fewer calories.
How long does the effect of gastric botox last, and is weight loss guaranteed after the procedure?
The effect of gastric botox typically lasts between 4 and 6 months. At the end of this period, the effect of the botox completely wears off, and the stomach muscles return to their normal function. Gastric botox does not guarantee permanent weight loss. The weight loss after the procedure largely depends on how well the patient adheres to a post-procedure diet and exercise program. Botox is only a supportive tool; it is not a permanent solution. Therefore, patients should view the procedure as a starting point and use this period to transform it into a lifestyle change. Otherwise, the risk of returning to old eating habits and regaining weight is very high once the effect of the botox has passed.
What is the success rate of this procedure when not supported by diet and exercise?
The success rate of the gastric botox procedure is quite low when it is not supported by a healthy diet and regular exercise. Botox only physically slows down the rate of stomach emptying and increases the feeling of fullness, but it does not solve the patient’s psychological eating habits, emotional eating issues, or poor nutritional choices. If the patient does not take advantage of the opportunity provided by botox and continues to consume high-calorie, unhealthy foods, the expected weight loss will not occur. In some cases, there may be no weight loss at all or very little weight loss. Therefore, gastric botox should not be seen as a miracle solution on its own but must be applied as part of a lifestyle change program.
For which BMI range of patients is gastric botox a more suitable weight control method?
Gastric botox is generally suitable for patients who are not candidates for surgical intervention or who are looking for a milder weight control method. This procedure is an ideal option for individuals, typically with a BMI between 27 and 35, who are not diagnosed with surgical obesity but want to lose weight. Patients in this group are generally classified as moderately overweight or mildly obese. For severely obese patients with a BMI over 40, gastric botox is usually not sufficient to provide significant weight loss on its own, and surgical methods (gastric sleeve, bypass, etc.) are considered more effective for this group. Therefore, botox serves as a bridge for patients who are looking for a non-surgical and temporary solution.
What are the potential side effects and minor complications that may arise during or after the procedure?
Although the gastric botox procedure is generally considered safe, some minor side effects and potential complications may occur during or after the procedure. The most common side effects include mild abdominal pain, nausea, bloating, indigestion, and temporary constipation. These symptoms usually resolve on their own within a few days and do not significantly affect the patient’s comfort. Serious complications, such as the spread of botox outside the stomach or infection at the injection site, are extremely rare. To minimize these risks, it is of great importance that the procedure is performed by an experienced gastroenterologist in a sterile environment.
Why should gastric botox not be administered to individuals with allergies or muscle diseases?
Gastric botox should absolutely not be administered to individuals with a known allergy to botulinum toxin or those with muscle diseases like myasthenia gravis. Botulinum toxin is a neurotoxin that temporarily paralyzes muscles. In muscle diseases like myasthenia gravis, the communication between nerves and muscles is already impaired, and the application of botox can worsen the symptoms of the existing disease and create serious health risks. In individuals with allergies, serious allergic reactions, and even life-threatening conditions like anaphylactic shock, can occur. Therefore, before the procedure, the patient’s medical history, allergies, and all existing diseases must be examined in detail, and the risk factors should be taken into consideration.
What temporary effects does the relaxation of stomach muscles after the procedure have on the digestive system?
The relaxation of stomach muscles after the gastric botox injection causes some temporary effects on the digestive system. The most prominent effect is the slowing down of the gastric emptying rate. This causes food to stay in the stomach for a longer time, making the patient feel full for a longer period. However, this situation can also lead to digestive problems such as mild bloating, indigestion, or stomach discomfort in some patients. The slow working of the stomach muscles can cause the overall digestive process to slow down, which can temporarily lead to issues like constipation. These effects usually subside within a few days to a week and return to normal as the patient’s body adjusts to the new situation.
Is there a risk of gastric botox injections being unsuccessful, and what are the possible reasons for this?
Yes, there is a risk of gastric botox injections being unsuccessful. One of the most common reasons for this is that the injection is not performed at the correct points on the stomach wall or the injection is not deep enough. Expertise and experience are of great importance at this point. Also, the use of a low-quality botox product or the toxin having lost its effectiveness can also lead to failure. In rare cases, some patients’ bodies may have developed resistance to botox. This can cause the drug’s effect on the muscles to be less than expected or non-existent. For a successful outcome, the experience of the doctor performing the procedure, the quality of the materials used, and the correct evaluation of the patient’s anatomical structure are critical factors.
What kind of comfort does the gastric botox procedure provide to the patient by not requiring general anesthesia?
The fact that the gastric botox procedure does not require general anesthesia provides a significant comfort and safety advantage to the patient. The procedure is usually performed under light sedation, with the patient conscious or in a light sleep state. This eliminates the risks associated with general anesthesia (breathing problems, allergic reactions, etc.). Patients do not have to go to the operating room and undergo a long recovery period. A very short rest period after the procedure is sufficient, and patients can usually return to their daily activities within a few hours. This quick recovery time is a great advantage for patients who do not want to take a break from their work or social life. The ease of the procedure also increases patients’ motivation for treatment.
How do gastric sleeve and gastric botox differ in terms of achieving weight loss goals?
Gastric sleeve and gastric botox fundamentally differ in terms of permanence and degree of effect in achieving weight loss goals. Gastric sleeve surgery creates a permanent anatomical change that physically limits the patient’s eating capacity and lowers hunger hormone levels. This provides a much more significant and long-term weight loss for patients with higher BMIs. Gastric botox, on the other hand, is a non-surgical, temporary procedure. It slows down the gastric emptying rate to increase the feeling of fullness, but this effect only lasts for 4-6 months. Gastric botox offers short-term support for patients who target less weight loss and are not suitable for surgery. Therefore, while sleeve gastrectomy is a permanent solution for severe obesity, botox is a starting point for mild to moderate excess weight.
In what situations should a patient prefer gastric sleeve surgery for a permanent solution, and in what situations should they opt for botox, a temporary and less invasive method?
A patient should prefer gastric sleeve surgery if they are morbidly obese (BMI 40 and over) or have serious comorbidities related to obesity (BMI 35-39.9) and are targeting a permanent and significant weight loss that will fundamentally change their quality of life. On the other hand, if the patient does not want to take surgical risks, has a BMI below 35, and is struggling to lose weight with just diet and exercise, or wants to lose a small amount of weight (10-15 kg), then gastric botox is a more suitable option. Gastric botox can also be considered as an intermediate solution for people preparing for a surgical operation or those with a fear of surgery. In both situations, a doctor’s comprehensive evaluation is essential for making the right decision.
Compared to gastric sleeve surgery, what are the main differences between the recovery process and hospital stay duration of gastric botox?
Since gastric sleeve surgery is a major surgical operation performed under general anesthesia, the patient’s recovery process can take several weeks, and they usually need to stay in the hospital for 1-3 days. The patient’s body needs time to heal after the surgery and adapt to the new diet. In contrast, gastric botox is an endoscopic, non-surgical procedure with an almost zero recovery time. Patients can be discharged shortly after the procedure and can return to their normal lives within a few hours. There is almost no hospital stay, as the procedure is performed on an outpatient basis. This key difference makes gastric botox a much more attractive option for patients with a busy work schedule or who cannot afford a long recovery period.
What alternatives can be recommended to a patient who is suitable for gastric sleeve surgery but does not want to take surgical risks?
For a patient who is suitable for gastric sleeve surgery but does not want to take surgical risks, less invasive or non-surgical alternatives can be recommended. These alternatives include endoscopic methods such as the gastric balloon and gastric botox. The gastric balloon is a device placed inside the stomach that mechanically creates a feeling of fullness. Both of these help the patient learn portion control and provide a starting point for weight loss. Additionally, personalized nutrition and exercise programs supported by intensive dietitian follow-up can also be an option. Although these methods are not as effective as surgery, they can be a safe and effective stepping stone for the patient to start a healthy weight loss journey.
When deciding which method is more suitable for a patient, what factors do doctors pay the most attention to?
When deciding which method is more suitable for a patient, doctors pay attention to several critical factors. The first of these is the BMI value and the patient’s degree of obesity. This is the initial screening criterion. Secondly, the presence of comorbidities related to obesity (diabetes, hypertension, etc.) is evaluated. Thirdly, the patient’s overall health status and whether they are suitable for any type of surgery are examined. Fourthly, the patient’s psychological state and their ability to adapt to lifestyle changes are taken into consideration. Finally, the patient’s weight loss goals and the success of previous weight loss attempts also influence the decision-making process. All of these factors are evaluated as a whole to determine the most suitable, safest, and most effective treatment plan for the patient.